
Intravenous Detoxification Therapy for Substance Use Disorder
Intravenous (IV) detoxification therapy has emerged as a promising adjunctive treatment for substance use disorder, offering targeted support for the body's natural detoxification processes. This article examines the mechanisms by which IV detox drips, containing key components such as glutathione, acetylcysteine, silybin, glycyrrhizin, alpha-lipoic acid, curcumin, B-complex vitamins, taurine, high-dose vitamin C, amino acids, and ginkgo biloba extract, facilitate the elimination of substances including cannabis, morphine, methamphetamine, ketamine, and MDMA from the human body.
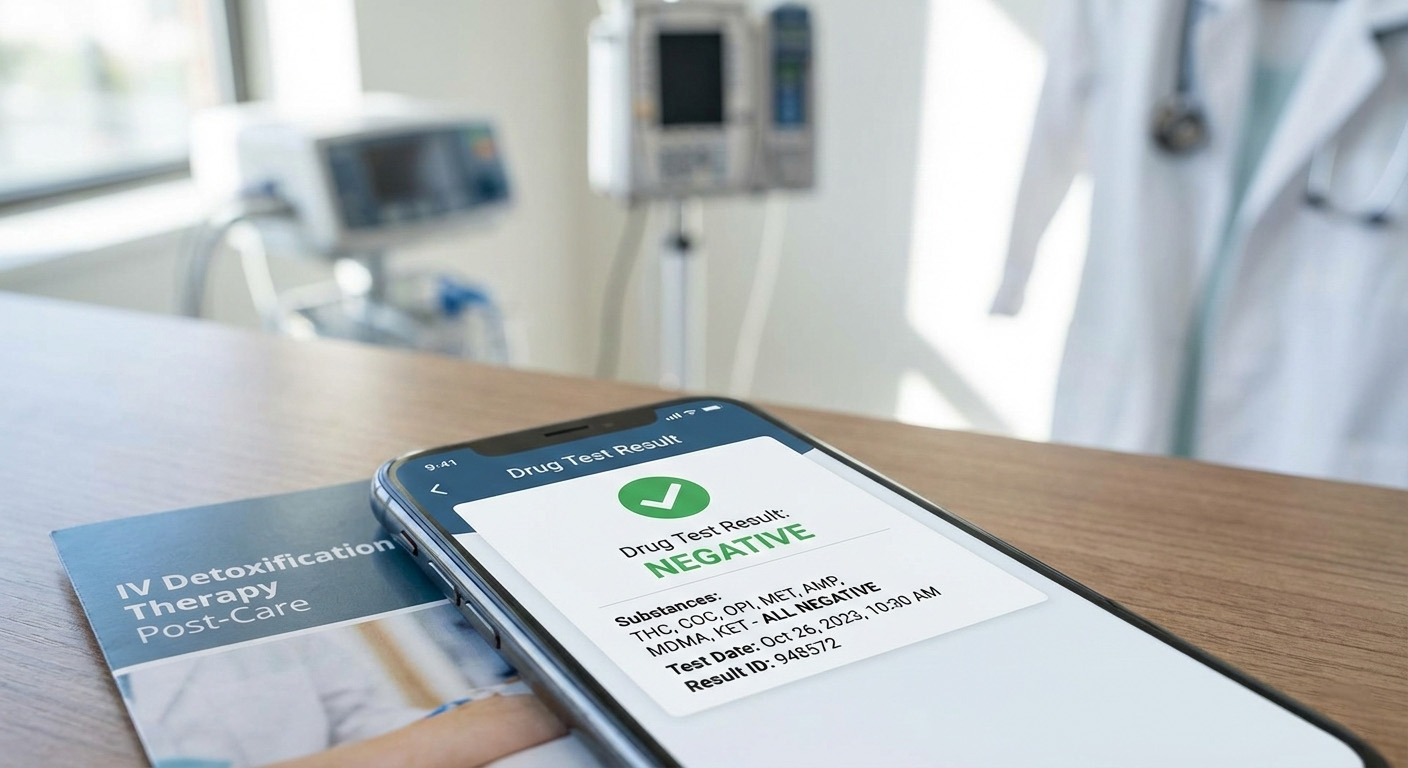
After Intravenous (IV) detoxification therapy, the drug test result should turn negative within 48 hours.

Introduction
The detoxification process following substance use involves multiple physiological pathways, primarily centered in the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal system. IV detoxification therapy provides bioavailable nutrients directly to these systems, enhancing their capacity to metabolize and excrete xenobiotics. This article explores the specific mechanisms through which each component contributes to the detoxification of commonly abused substances.
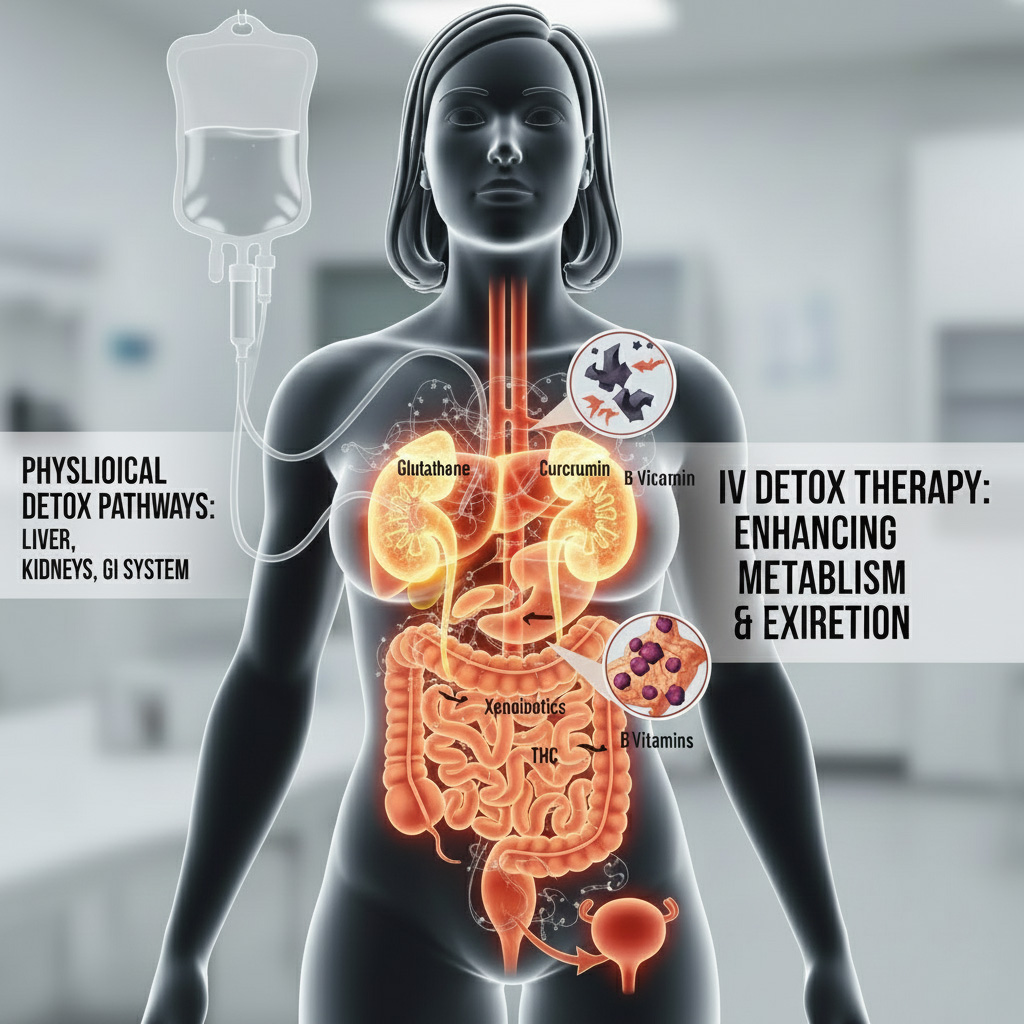
Key Components and Their Detoxification Mechanisms
Glutathione (GSH)
Glutathione, the body's primary antioxidant, plays a critical role in phase II biotransformation reactions. It conjugates with reactive intermediates of drug metabolism, forming water-soluble glutathione-S-conjugates that are readily excreted via bile and urine. For cannabis metabolites, particularly tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) glucuronides, glutathione enhances their solubility and elimination. In methamphetamine detoxification, GSH neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during catecholamine depletion, protecting hepatocytes from oxidative damage.
Acetylcysteine (NAC)
Acetylcysteine serves as a precursor for glutathione synthesis, increasing intracellular GSH levels by providing cysteine, the rate-limiting amino acid in GSH biosynthesis. NAC has been shown to reduce oxidative stress in morphine-dependent individuals by restoring GSH levels depleted by chronic opioid use. Additionally, NAC modulates glutamate receptors, which may help alleviate cravings associated with ketamine and MDMA use.
Silybin (Milk Thistle Extract)
Silybin, the active component of silymarin, exhibits hepatoprotective properties through multiple mechanisms. It stimulates hepatocyte regeneration, inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in drug metabolism, and enhances glutathione synthesis. In cannabis detoxification, silybin upregulates UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), accelerating the conjugation and elimination of THC metabolites. For methamphetamine users, silybin protects against hepatotoxicity induced by catecholamine oxidation products.
Glycyrrhizin (Licorice Root Extract)
Glycyrrhizin possesses anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective properties. It inhibits 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, increasing cortisol levels which enhances hepatic drug metabolism. Glycyrrhizin also modulates the expression of multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs), facilitating the efflux of drug metabolites from hepatocytes. In MDMA detoxification, glycyrrhizin reduces serotonin toxicity by inhibiting monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA)
Alpha-lipoic acid functions as a potent antioxidant and metal chelator. It regenerates other antioxidants including vitamin C, vitamin E, and glutathione, creating a synergistic detoxification effect. ALA enhances mitochondrial function, improving energy metabolism in cells damaged by chronic substance use. For ketamine users, ALA protects against NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity and reduces oxidative stress in the central nervous system.
Curcumin (Turmeric Extract)
Curcumin exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective properties. It activates the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, upregulating antioxidant response elements (AREs) and phase II detoxification enzymes. Curcumin has been shown to reduce morphine tolerance and dependence by modulating opioid receptors and reducing neuroinflammation. In cannabis detoxification, curcumin enhances fatty acid oxidation, promoting the breakdown of THC stored in adipose tissue.
B-Complex Vitamins
B-complex vitamins, including thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pyridoxine (B6), folate (B9), and cobalamin (B12), serve as essential coenzymes in drug metabolism pathways. Thiamine deficiency is common in chronic alcohol and opioid users, and supplementation prevents Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Pyridoxine is critical for catecholamine synthesis and metabolism, supporting the recovery of dopamine and serotonin systems depleted by methamphetamine and MDMA use.
Taurine
Taurine, a sulfur-containing amino acid, acts as an osmolyte and antioxidant. It modulates GABA and glutamate receptors, reducing excitotoxicity associated with substance withdrawal. Taurine enhances mitochondrial function and protects against oxidative stress in the brain and liver. For ketamine users, taurine reduces NMDA receptor hyperexcitability during withdrawal, alleviating cognitive deficits.
High-Dose Vitamin C
High-dose vitamin C functions as a reducing agent, enhancing the solubility and elimination of drug metabolites. It regenerates vitamin E and glutathione, creating a potent antioxidant network. Vitamin C enhances iron absorption, supporting hemoglobin synthesis in individuals with anemia related to chronic substance use. In MDMA detoxification, vitamin C protects against serotonin depletion and oxidative damage to serotonergic neurons.
Amino Acids
Essential and non-essential amino acids provide building blocks for protein synthesis and neurotransmitter production. Methionine serves as a methyl donor in phase II methylation reactions, facilitating the elimination of drug metabolites. Tyrosine and phenylalanine support catecholamine synthesis, helping restore dopamine and norepinephrine levels depleted by methamphetamine use. Tryptophan provides the precursor for serotonin synthesis, aiding recovery from MDMA-induced serotonergic damage.
Ginkgo Biloba Extract
Ginkgo biloba extract, rich in flavonoids and terpenoids, improves cerebral blood flow and protects against oxidative stress. It modulates glutamate receptors and enhances antioxidant defenses in the brain. Ginkgo biloba has been shown to improve cognitive function in cannabis users by reducing cannabinoid-induced memory impairment. For methamphetamine users, ginkgo biloba protects against dopaminergic neurotoxicity and improves motor function.
Substance-Specific Detoxification Pathways
Cannabis (THC)
THC undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver, primarily via cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4) to form 11-hydroxy-THC (11-OH-THC), which is further oxidized to 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC (THC-COOH). IV detox components enhance this process by:
- Upregulating UGT enzymes for glucuronidation (silybin, curcumin)
- Increasing glutathione availability for conjugation reactions (GSH, NAC)
- Enhancing fatty acid oxidation to release stored THC (curcumin, ALA)
- Improving hepatic function and bile flow (silybin, glycyrrhizin)
Morphine and Opioids
Morphine is metabolized by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases to form morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G) and morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G). IV detox supports this process through:
- Restoring glutathione levels depleted by chronic opioid use (NAC, GSH)
- Reducing oxidative stress in the liver and brain (ALA, vitamin C)
- Modulating opioid receptors and reducing dependence (curcumin, taurine)
- Supporting mitochondrial function and energy metabolism (B vitamins, amino acids)
Methamphetamine (Meth)
Methamphetamine is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP2D6, CYP3A4) to form amphetamine and para-hydroxymethamphetamine. The detoxification process involves:
- Neutralizing ROS generated during catecholamine oxidation (GSH, ALA, vitamin C)
- Protecting dopaminergic neurons from neurotoxicity (ginkgo biloba, curcumin)
- Supporting dopamine synthesis and reuptake (B vitamins, tyrosine)
- Enhancing hepatic metabolism and excretion (silybin, glycyrrhizin)
Ketamine
Ketamine is metabolized in the liver by CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 to form norketamine and dehydronorketamine. IV detox supports recovery by:
- Modulating NMDA receptor function (taurine, ginkgo biloba)
- Reducing excitotoxicity and oxidative stress (ALA, vitamin C)
- Improving cognitive function and memory (ginkgo biloba, B vitamins)
- Supporting liver function during metabolism (silybin, glycyrrhizin)
MDMA (Ecstasy)
MDMA is metabolized by CYP2D6 to form 3,4-dihydroxymethamphetamine (HHMA), which undergoes methylation and glucuronidation. The detoxification process involves:
- Protecting serotonergic neurons from oxidative damage (vitamin C, ALA)
- Supporting serotonin synthesis and reuptake (tryptophan, B vitamins)
- Reducing neuroinflammation (curcumin, glycyrrhizin)
- Enhancing conjugation and elimination of metabolites (GSH, NAC)
Clinical Considerations
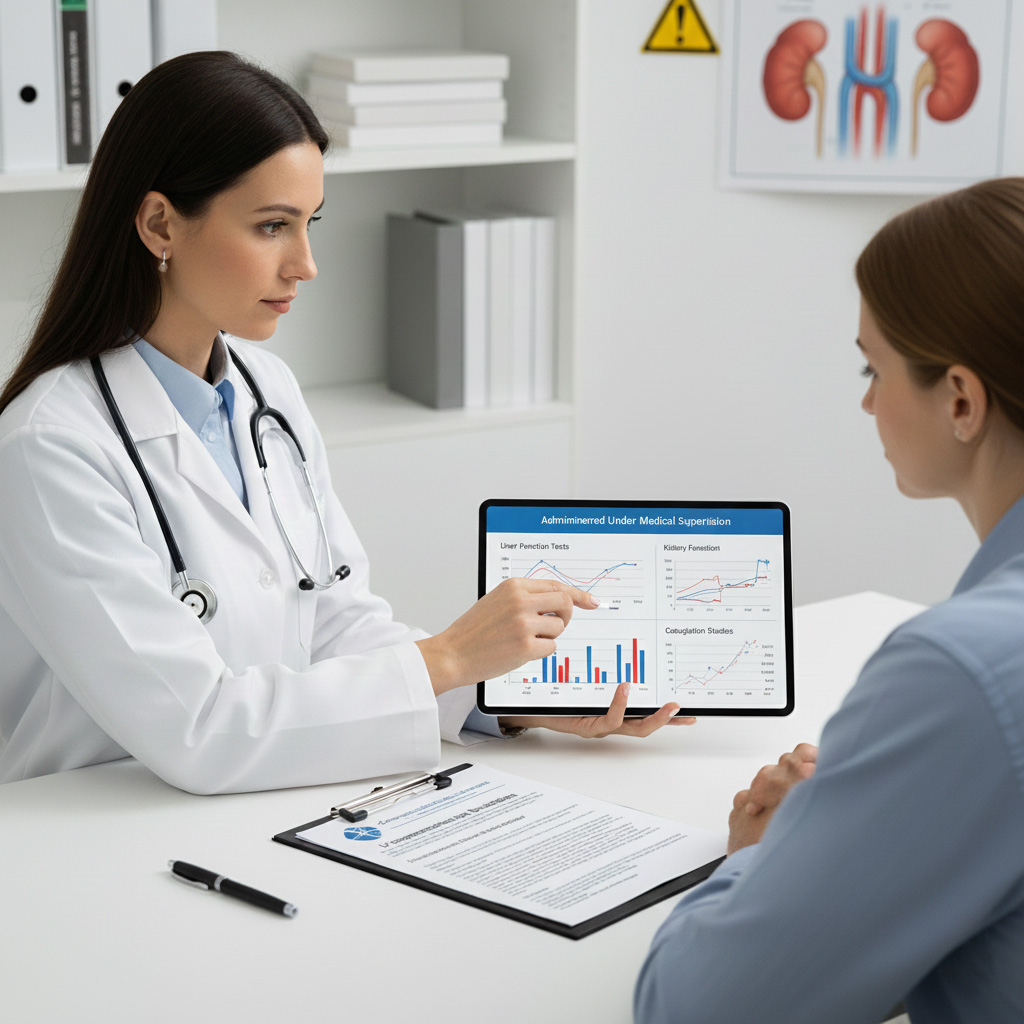
IV detoxification therapy should be administered under medical supervision, as high doses of certain components may cause adverse effects. Vitamin C in high doses can cause oxalate nephropathy in susceptible individuals. Glycyrrhizin may cause electrolyte imbalances and hypertension with prolonged use. NAC can cause anaphylactoid reactions in rare cases.
Patients should undergo comprehensive medical evaluation prior to treatment, including liver and kidney function tests, electrolyte panels, and coagulation studies. Treatment protocols should be individualized based on the substance used, duration of use, and patient's overall health status.

Conclusion
IV detoxification therapy represents a valuable adjunctive treatment for substance use disorder, providing targeted nutritional support for the body's natural detoxification processes. The combination of antioxidants, hepatoprotective agents, vitamins, and amino acids works synergistically to enhance the elimination of various substances while protecting against their toxic effects. Further research is needed to establish optimal treatment protocols, dosages, and duration for different substances and patient populations.
Contact Info
Address
Josef-Dietzgen-Str.3, 53773 Hennef, Germany
Copyright 2025, All rights reserved.